Generative AI is like a magic artist. It learns from a lot of examples and then uses that learning to create new things that fit the patterns it learned. It’s like having a creative computer friend that can make up new music, art, or even stories!
Generative AI (GenAI) is a type of artificial intelligence that is used to generate new data or content from existing data. It can be used to create new text, images, videos, and other forms of data.
Large Language Models are a type of generative AI that use deep learning algorithms to generate natural language from large datasets. They are used for a variety of applications such as natural language processing, machine translation, and question answering.
Large Language Modal (LLM) Use Cases
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 have a wide range of use cases across various industries and domains. Here are some prominent use cases:
- Content Generation:
- Writing articles, blog posts, and reports.
- Creating marketing copy and advertising content.
- Drafting emails and messages.
- Conversational Agents:
- Developing chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Enabling natural language interactions in customer support.
- Language Translation:
- Translating text between different languages.
- Facilitating real-time language translation for travelers and businesses.
- Text Summarization:
- Summarizing lengthy documents, research papers, and articles.
- Generating concise overviews for news stories.
- Code Generation:
- Writing code snippets in various programming languages.
- Assisting developers in automating repetitive tasks.
- Creative Writing:
- Crafting poetry, stories, and screenplays.
- Generating unique content for artistic purposes.
- Educational Tools:
- Providing explanations and answers for students’ questions.
- Offering tutoring and learning assistance.
- Data Analysis:
- Assisting in data interpretation and insights generation.
- Simplifying complex statistical information for non-experts.
- Medical and Scientific Applications:
- Analyzing medical records and generating clinical reports.
- Assisting researchers in data analysis and hypothesis generation.
- Legal and Compliance:
- Drafting legal documents, contracts, and agreements.
- Offering legal research and analysis support.
- Personal Assistants:
- Managing calendars and scheduling appointments.
- Sending reminders and setting alarms.
- Gaming and Entertainment:
- Generating in-game dialogues and narratives.
- Creating interactive storytelling experiences.
- Accessibility Support:
- Assisting individuals with disabilities in communication and information access.
- Market Research and Analysis:
- Extracting insights from social media and online discussions.
- Analyzing consumer sentiment and trends.
- Simulations and Training:
- Simulating characters and scenarios for training purposes.
- Enhancing virtual reality experiences.
- Human Resources:
- Assisting in resume writing and job description creation.
- Conducting initial candidate screenings.
- Innovative Interfaces:
- Enabling voice-controlled applications and devices.
- Powering interactive storytelling experiences.
- Knowledge Management:
- Assisting in documentation, note-taking, and knowledge retrieval.
- Organizing and summarizing research materials.
- Automated Social Media:
- Generating social media posts and engagement.
- Providing suggestions for content creation.
- Ethical and Societal Debates:
- Engaging in philosophical discussions and debates on ethical issues.
- Promoting critical thinking and diverse perspectives.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of Large Language Models. As the technology evolves, new use cases will likely continue to emerge.
What is a Foundation Model?
A foundation model is a large-scale language model trained on vast amounts of data and designed to perform a wide range of tasks. These models are evaluated using diverse prompts across many scenarios, enabling them to generalize effectively and adapt to various downstream applications such as text generation, summarization, translation, and more.
Key Characteristics of GPT-4 Foundation Model
1. Scale and Architecture
GPT-4 is built using a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, comprising 1.76 trillion parameters across 120 layers This is more than 10 times the size of GPT-3. The model routes inputs through a subset of 2 out of 16 expert networks per forward pass, optimizing performance and cost.
2. Training Data
GPT-4 was trained on approximately 13 trillion tokens, sourced from a mix of datasets including CommonCrawl, RefinedWeb, and other curated sources. It also includes data from platforms like Twitter, Reddit, YouTube, and a large collection of textbooks and code repositories
3. Generative Capabilities
GPT-4 is a generative model, capable of producing original, contextually relevant content. It can:
- Write essays and articles
- Generate computer code
- Create charts and websites from text descriptions
- Compose emails, summaries, and more
4. Human-like Interaction
GPT-4 maintains context across interactions, remembering previous prompts and adapting to new inputs. This enables natural, conversational exchanges, similar to human dialogue.
5. Adaptability
Through continuous interaction, GPT-4 learns patterns and relationships, improving its responses over time. This adaptability reduces the need for retraining for each new task.
6. Self-supervised Learning
GPT-4 uses self-supervised learning, allowing it to train on unlabeled data. This approach enables the use of massive raw datasets, shifting the focus from manual labeling to computational scalability.
7. Multi-modal Learning
GPT-4 supports multi-modal inputs, including text and images, enabling it to interpret and generate content across different data types. This mimics human-like sensory learning and expands its utility.
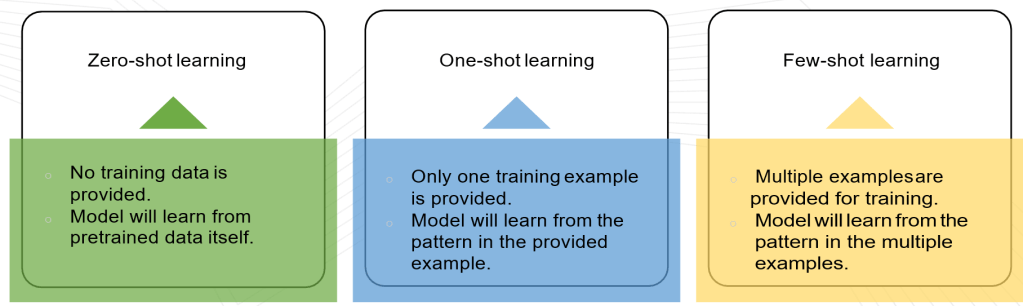
8. Few-shot and Zero-shot Learning
GPT-4 excels at few-shot and zero-shot learning, allowing it to perform tasks with minimal or no specific training examples. This makes it highly versatile and efficient for rapid deployment.
What are Prompts?
Generative AI models primarily interact with users through text-based input. You provide instructions or requests via a text interface, and the model works to fulfill them. In general, this input is called a prompt.
For large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or ChatGPT, prompts can range from straightforward questions (e.g., “Who is the president of the India?”) to complex tasks (e.g., “Analyze the impact of globalization on the development of third-world countries, focusing on economic, political, and social aspects.”). Prompts may also include various forms of data—even files such as CSVs—or be as casual and open-ended as “Tell me a joke. I’m feeling down today.”
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt Engineering is a relatively new field focused on creating and refining prompts to make the most effective use of language models (LMs) across various applications and research areas. Developing these skills helps users understand both the strengths and limitations of large language models (LLMs).
It is applied by:
- AI professionals – converting tasks into prompt-based datasets that a model can be trained on.
- Researchers – enhancing LLM performance on a range of tasks from question answering to arithmetic reasoning.
- Developers – designing reliable prompting techniques to connect LLMs with other tools.
Types of Writing Prompts
- Instruction – Directly tells the model what to do.
Example: “Write a story about a poor, hardworking farmer who becomes a successful businessman through determination.” - Continuation – Provides a partial sentence or text for the model to complete.
Example:
Prompt: “The following is a step-by-step process for preparing chicken salad. Step 1: Cut the veggies –”
AI Response: “Step 2: Toss the chicken nuggets. Step 3: Mix everything together.” - In-Context Learning (ICL) – Supplies a few examples in the prompt, enabling the model to learn from them and apply the same logic to new inputs.
Example: Providing short passages with labeled topics so the AI can classify a new passage correctly.
Delimiters in Prompts
A delimiter is a symbol or marker used to separate sections within a prompt. It:
- Organizes information for clarity.
- Marks where tasks or sections begin and end.
- Helps the AI focus on specific parts of the prompt.
- Often works with a stop sequence (e.g.,
\n,###,===,::).
Benefits of Delimiters
- Improved Control – Focus the model on the right section of text.
- Multi-Turn Conversations – Separate user inputs from AI responses for coherent dialogues.
- Task Separation – Divide multiple tasks (e.g., summarization, translation) within one prompt.
- Context Preservation – Maintain conversation flow in interactive sessions.
- Simultaneous Prompts – Handle multiple requests in one input for batch responses.
- Customization – Use custom delimiter tokens to suit specific needs.
Example:
Task1: Summarize === “Healthy ecosystems require a variety of species…”
Task2: Translate === “Hello, how are you?”
Here,===clearly separates tasks so the AI can respond to each one independently.
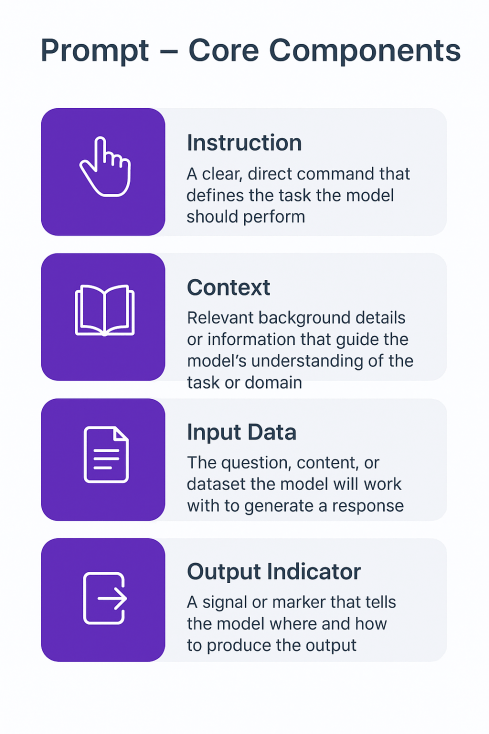
Elements Of Prompts
A prompt can include several components, but not all are always necessary. The structure and combination of these elements should be tailored to the specific task or objective.
Key processes in prompt engineering
There are three main processes to follow in prompt engineering:
Types Of Prompts
- Open Ended Prompts: An Open-ended prompt requires the model to generate an answer with few constraints or options given by the prompt.

2. Closed Type: A Closed-ended prompt asks the model to complete an action on a text, given specific parameters and instructions.
| Prompt Type | Description | Example |
| Rewrite | Modify the existing content to suit different variations such as form, tone, persona, etc. | Infuse a cheerful tone into this blog. |
| Extract | Extract a specific block of text verbatim from the given content. | Identify the sentence where the doctor recommended the treatment plan. |
| Summarize | Involves summarizing a block of text while avoiding the use of exact wording from the original text. | Summarize the key tasks from this conference report. |
| Closed ended QA | This entails extracting information from a written text, which can be either extractive or abstractive in nature. | How frequently did Alice discuss her new project in this conversation? |
| Close ended classification | Requesting the model to categorize a given text based on a provided selection of classes. | Categorize the content as either Travel, Fashion, or Entertainment. |
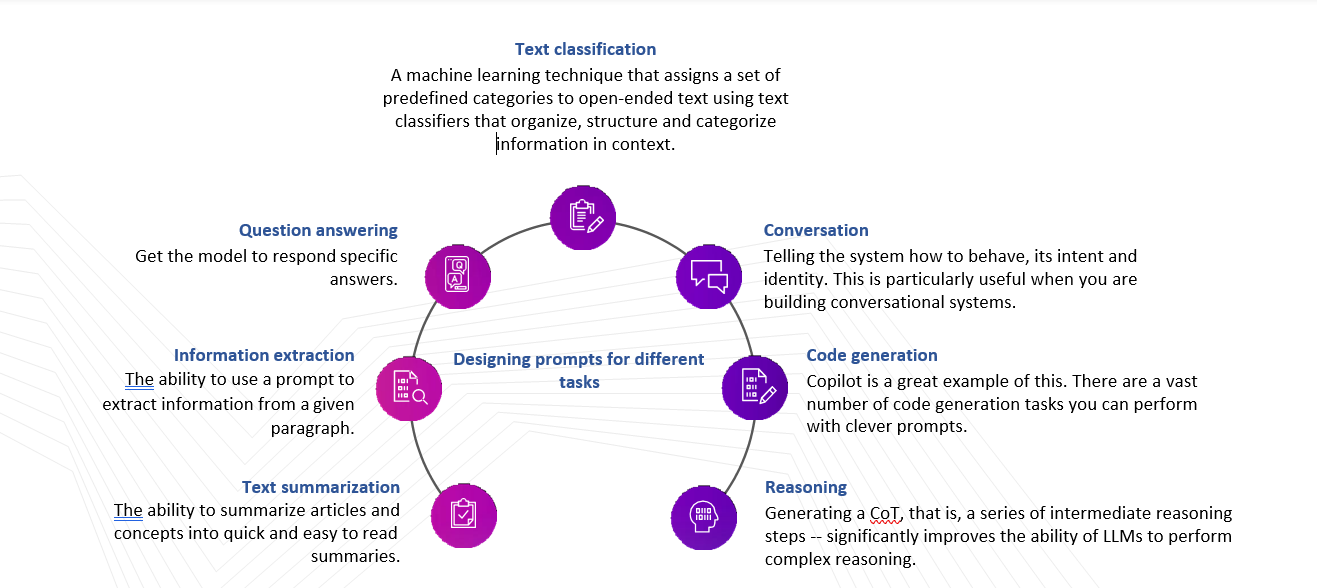
Designing prompts for different tasks
A prompt can contain information like the instruction or question you are passing to the model and include other details such as inputs or examples. Today’s LLMs can perform all kinds of advanced tasks that range from text summarization, mathematical reasoning, to code generation. Well-crafted prompts can be used to perform all types of interesting and different tasks.
Note: This is just very beginning introduction of GenAI. To complete content and knowledge you may DM me on er.sandeepp@gmail.com directly or you may join my live sessions for the same.
You may join my WhatsApp group for further notification about boot camp : https://chat.whatsapp.com/JTnI8LL9FgrI4G8Qcm68fq

